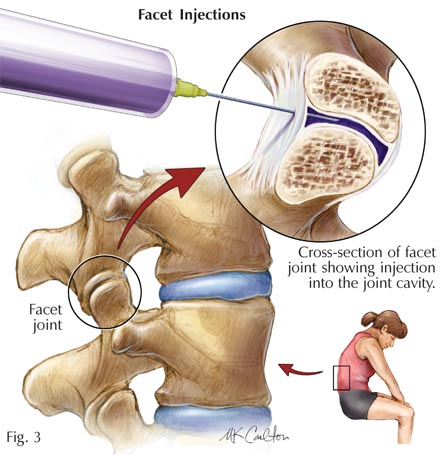
A thoracic sprain (TSCI), also known as a T9 spinal injury, is damage to the thoracic spine or other structures in the thoracic region, which leads to numbness and limited range of motion, pain and weakness. A limited injury causes only localized numbness, whereas a wide area can cause more serious damage to the spine. Thoracic injuries are caused by a variety of physical forces, such as trauma, falls, repetitive motions, muscle strains, and trauma to adjacent structures.
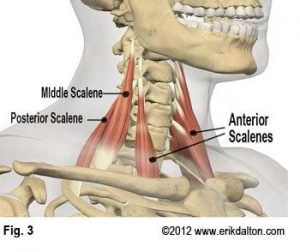
Muscle spasms can result from muscle pulls on the cervical discs between the vertebrae of the thoracic spine
These pulls may occur during a twisting or extension exercise, such as a seated bicycle or an elliptical trainer. It may also be an injury to the discs in the disc herniation, which occurs when a disk is bulging out of its socket in the thorax. The strain on the discs and other structures may cause tears, dislocations, or breaks to the muscles and ligaments in the thoracic region.
When a person suffers a thoracic spinal injury, the first step is to get a proper diagnosis. Although this type of injury occurs rarely, it can occur suddenly and unexpectedly. In fact, the most common causes of a thoracic injury are repetitive movements, such as lifting heavy objects.
Sometimes, a spinal cord injury can result from a traumatic accident, such as a motorcycle collision, motorbike accident, or car crash, where the force of an impact to the head, neck or spinal cord creates a blow to the nerve roots. This can result in tingling sensations or numbness in the face, arm or hand. This type of injury can cause weakness and lack of coordination and range of motion in both the upper and lower limbs. Other times, an injury to the nerve roots causes weakness or paralysis in one or more of the legs. In addition to the motorway injury, muscle sprains or tears to the muscles and ligaments of the trunk and legs can also cause injury to the nerve roots of the spine.
Thoracic spasms result when the muscle spasms interrupt normal spinal movement. They are usually accompanied by decreased bladder and bowel control, nausea, vomiting, sweating, chest pain, dizziness, chest pain, difficulty breathing, constipation, nausea and vomiting, headaches, difficulty swallowing, and increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, and irregular heart beats, among others.
The symptoms of a muscle spasm are usually worse the moment the symptoms start to appear
Muscle spasms can last for a number of hours or for a few days, sometimes even up to several weeks, but will often disappear on their own. However, they can persist for days, weeks, or even months. Thoracic muscle spasm can be disabling to a degree and sometimes may require surgery to relieve the patient's pain.
The most important symptom that distinguishes muscle spasm from other types of muscle injuries is the location of the injury. A muscle spasm occurs in the thoracic region when the muscle is stretched to more than 30 degrees of flexion, as opposed to a simple bursa.
Although symptoms may not appear immediately after the injury, it's important to visit a doctor as soon as possible to make sure your condition is improving, since an injury like this can lead to more complications if not treated promptly. To increase your chance of recovery, you should receive treatment as quickly as possible, to reduce the likelihood that the damaged area will heal on its own or that you'll become handicapped due to further damage.
The most common symptom is difficulty breathing. If you don't breathe correctly after suffering from thoracic muscle spasm, you may experience difficulty talking or swallowing, both of which could cause you to lose consciousness and even cause death in certain cases. A doctor may prescribe oxygen therapy, which helps to improve your breathing, as well as intravenous fluids and antibiotics.
Another common complaint after a thoracic injury is pain in the chest or back. Sometimes pain is associated with abdominal trauma as well, but if it's only in one or both sides of the body, it may indicate another problem. The pain is often so severe that it makes walking or reaching a chair, or table painful, especially if you have a stiff neck.
If you believe you have suffered a thoracic spasm, contact a doctor immediately to determine the cause. Don't wait until you feel any symptoms to seek help; you could seriously injure or even kill yourself.